A three-page order issued July 16 lays out the scope of the cuts and next steps. Operating under the assumption that field enforcement “should be concentrated in urban areas where the need for them is greatest,” the order closes 11 of 24 offices outright and will initially result in a net reduction of six employees. These regional offices will be supplemented by two “tiger teams” stationed in Maryland and Colorado.
Going forward, field agents will also need to be certified electrical engineers, and the Enforcement Bureau wants to invest money in “remotely-operated” and portable spectrum-monitoring systems to serve its new primary mission: “the enforcement of the Commission’s radiofrequency interference requirements and other key rules.” Continue reading “FCC Field Plan Redux; Anti-Pirate Policy Discussion Underway”
Radio in Times of Crises
When flooding rains pounded Texas earlier this summer, many communities found themselves in crisis. With wired network infrastructures flooded and unusable and power a sometimes-thing draining the battery-packs at cell tower-sites, many Texans found themselves reaching for their radio to find out what was going on.
One area that was hit very hard by the rains was Austin and surrounding towns, including Wimberley, Texas: flash-flooding sent a wall of water down the Blanco River in the Wimberley Valley on Memorial Day weekend that swept away entire structures, killing several people and doing millions of dollars in damage. Just a couple of years earlier, folks there had founded a non-profit organization to apply for an LPFM license. Construction permit in hand, when the rains came and wiped out most other community communications they did not stand idly by. Continue reading “Radio in Times of Crises”
In the Wake of Prometheus, Media Ownership Still Sucks
The following is a guest commentary by friend and colleague Dr. Christopher Terry, a Lecturer of Media Law and Policy in the Department of Journalism, Advertising and Media Studies at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. He spent more than 15 years as a producer in commercial radio. His dissertation examined more than 1000 FCC media ownership decisions between 1996-2010, and he has published quite a bit on media diversity, political advertising and of course, media ownership policy. Contact him via e-mail or Twitter
Today marks four years have since the 3rd Circuit handed down a second remand of the FCC’s media ownership policy in Prometheus Radio Project v. FCC. I thought we might take the opportunity of this anniversary to discuss how radio got so bad.
On February 8th, 1996, President Bill Clinton signed into the law the 1996 Telecommunications Act. Provisions within the Telecommunications Act implemented significant changes the legal, policy and social dynamics of media ownership. Although these changes could be felt across the media spectrum, the radio industry was fundamentally changed by the FCC’s implementation of the legislation. Continue reading “In the Wake of Prometheus, Media Ownership Still Sucks”
AM Broadcasters Still Seek Translators, Digital Authorization
When the FCC announced the creation of an “AM Revitalization Initiative” in 2013, the proposal included a grab-bag of industry desires, such as the right for AM stations to utilize FM translators and for AM stations to move from hybrid analog/digital broadcasting to the all-digital AM-HD protocol. But to the consternation of industry lobbyists and HD-backers there’s been no movement on this initiative — so now they’re beginning to whine about it.
Case in point is a commentary published in late June by Frank Montero, an attorney at D.C. communications law powerhouse Fletcher, Heald & Hildreth, which laments that AM broadcasters are being held hostage without access to FM translators and accuses the FCC of playing political football with the future of AM itself. It’s full of questionable assertions and revisionist history. Continue reading “AM Broadcasters Still Seek Translators, Digital Authorization”
O'Rielly Encourages War on Pirates
When FCC Commisioner Mike O’Rielly spoke last week to the summer conference of the New York State Broadcasters Assocaiation, he made pirate radio the lead-off topic, sending a clear signal that the Commission is responding to recent Congressional pressure and industry lobbying on the issue. How that response will manifest itself is yet to be determined, but any viable effort will have to involve thinking outside the box about how to be better spectrum-cops.
“Far from being cute, insignificant, or even somehow useful in the broadcasting ecosystem,” said O’Rielly, “pirate radio represents a criminal attack on the integrity of our airwaves, at a time when spectrum has become more scarce and precious than ever before.” He compared unlicensed broadcasters to “poison ivy in a neglected garden” and estimated that nearly one-quarter of all pirates in the country reside in the New York area (data, please!). Continue reading “O'Rielly Encourages War on Pirates”
New HD Radio Applications Seek to Fix System Flaws
There’ve been a couple of interesting developments out of the HD Radio trenches over the last few months. Both are touted as advanced “applications” for utilizing the HD Radio system — but in reality they’re band-aids that seek to fix fundamental flaws with the technology itself.
The first involves transmitter-manufacturer Nautel and its experiments with FM-HD multiplexing. This practice is inherent to the DAB/DAB+ radio systems adopted in Europe, Asia, and elsewhere: instead of every station having its own transmission infrastructure, stations send a stream to a multiplex transmitter where it’s combined with other stations and broadcast as a unifed signal. Instead of tuning to a particular frequency, DAB/DAB+ receivers look for the data-flags of the desired station and, once found, decode only that stream. In this configuration, DAB/DAB+ multiplexes can broadcast 10 or more channels of programming on a single unified digital radio signal. Continue reading “New HD Radio Applications Seek to Fix System Flaws”
FCC Radically Revises Enforcement Drawdown
Three months ago, the FCC announced it was preparing to decimate its Enforcement Bureau by removing half its existing staff from the field and closing two-thirds of its field offices. The proposal, based on a $700,000 study prepared by outside consultants, did not sit well with anybody, and was popularly seen as the FCC effectively abdicating its role as police on the public airwaves.
That is, until last Tuesday, when the FCC announced it was abandoning that plan. There will still be enforcement cuts, but nearly not as draconian. Nine field offices are slated to close (instead of 16) and the agency has pledged to concentrate its field staff in markets where maintaining spectrum integrity is of primary importance. To make up for the offices that will be closed, the FCC will have not one, but two “Tiger Teams” ready for deployment on a short fuse. Even though it was brief, Chairman Tom Wheeler’s statement on the revised plan sounds contrite: “This updated plan represents the best of both worlds: rigorous management analysis combined with extensive stakeholder and Congressional input.”
In simple terms, the broadcast industry lit a fire under Congress about the importance of having something akin to recognizable (if not robust) enforcement activity by the FCC. This is the fruit of a carefully-coordinated lobbying campaign by the National Association of Broadcasters, New York State Broadcasters Association, and New Jersey Broadcasters Association, and the hook they used to make their counterattack on the FCC’s downsizing plan was pirate radio. The subject was mentioned repeatedly in Congressional hearings during which the reduction-in-force came up. And on the day that the FCC announced it was stepping back from eviscerating enforcement, a letter co-signed by more than 30 members of Congress to the FCC was released highlighting “Unauthorized FM Radio Operations in New York City.” Continue reading “FCC Radically Revises Enforcement Drawdown”
CBRS: A Foray Into Spectrum Sharing
Earlier this spring the FCC announced the creation of what it calls the Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) — a swath of spectrum between 3.5-3.7 GHz that will be opened to both licensed and unlicensed services. This spectrum has traditionally been reserved for military radar and satellite uplinks; now it may become a sandbox for dynamic use of the public airwaves.
This particular slice of spectrum falls between two established Wi-Fi allocations, so one obvious potential use is for the provision of last-mile (or last-foot) broadband access. Incumbent users (the Navy and satellite ground stations) will remain on the band, but they’re so geographically sparse that for all intents and purposes this spectrum has been fallow in the majority of the United States. Under CBRS, instead of licensing devices to work on a particular channel within a band, they will be effectively permitted to use the entire band. The devices themselves will be programmed to sniff the local airwaves to find and utilize non-congested channels in its immediate area. Google is developing a database of CBRS users and devices that will be updated in real-time based on operating feedback from the devices themselves — the Internet of Things coming to life. Continue reading “CBRS: A Foray Into Spectrum Sharing”
In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?
Can’t say for sure, but the latest update to the Enforcement Action Database seems to suggest it, as the agency considers drastically cutting their already meager ranks. As of the end of April, there’ve been just 35 enforcement actions against 17 stations in four states. There has been no official report of field activity in May. In 2014, there were 52 enforcement actions in the same time-frame.
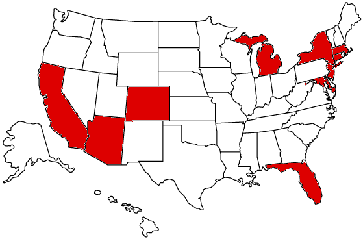 2014 saw the lowest level of FCC enforcement activity against unlicensed broadcasters in nearly a decade. Where agents are active, New York continues to lead the way, followed by New Jersey and California. A station in Colorado also got a warning letter this year, but that was a follow-up to a visit last year. Continue reading “In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?”
2014 saw the lowest level of FCC enforcement activity against unlicensed broadcasters in nearly a decade. Where agents are active, New York continues to lead the way, followed by New Jersey and California. A station in Colorado also got a warning letter this year, but that was a follow-up to a visit last year. Continue reading “In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?”
250-Watt LPFM "Upgrade" Petition Filed
This is the work of Michelle Bradley, the proprietor of REC Networks – arguably one of the most gifted FCC broadcast data-analysts in the country. REC’s been engaged with LPFM since its inception 15 years ago, and has tendered a petition for rulemaking to create an upgraded LP-250 station-class.
The premise is simple: 100 watts maximum power at just 100 feet above the ground doesn’t make for much of an FM signal. Many LPFM stations are difficult to receive indoors. REC starts off the petition with a litany of LPFM reception horror-stories (my favorite being the retirement facility in North Carolina where the local LPFM station can be heard on one side of the campus, but not the other). These vividly illustrate how LPFM’s current power/height restrictions work against stations being able to build viable and sustainable listenership and fiscal sponsorship. Continue reading “250-Watt LPFM "Upgrade" Petition Filed”