At the 2018 NAB Show in Las Vegas last month, FCC Chairman Ajit Pai highlighted the agency’s extensive efforts to combat unlicensed broadcasting. In addition to announcing that, in 2017, the agency issued “210 Notices of Unlicensed Operation” (I can only confirm 171), Pai said the agency “fined illegal broadcasters $143,800” (it’s actually $158,800) and “proposed fines totaling $323,688” (it’s actually $204,344). He also mentioned the recent raid of pirate stations in Boston, and reported “that we recently took similar action against a pirate operator in Miami and another operator in Queens, New York.”
 Considering that station-raids tend to generate a lot of publicity, both among local media in affected markets and in the radio industry trade-press, I was surprised that the Queens and Miami raids have not been reported on at all. This may be because they didn’t actually happen – or happened on dates and at times that don’t fit Chairman Pai’s narrative. In addition, further information has come to light that casts doubt on just how effective the FCC’s recent activity in Boston really was.
Considering that station-raids tend to generate a lot of publicity, both among local media in affected markets and in the radio industry trade-press, I was surprised that the Queens and Miami raids have not been reported on at all. This may be because they didn’t actually happen – or happened on dates and at times that don’t fit Chairman Pai’s narrative. In addition, further information has come to light that casts doubt on just how effective the FCC’s recent activity in Boston really was.
First, let’s break down the Queens case. This involves a guy by the name of Jose Luis Gerez and a station he used to run (and actually may still be running) called “Mambo FM.” According to an unsealed complaint dated last November, this station first appeared on the FCC’s radar in July 2013, when agents in the New York field office observed “what appeared to be an unlicensed broadcast station operating at 95.1 MHz in Queens, New York.” They tracked the signal to an apartment building on Gleane Street, less than a three-mile drive from LaGuardia Airport. After interviewing the superintendent of the apartment building, agents found an FM antenna on the roof with a coaxial cable running into the basement, where a transmitter and desktop computer providing the station’s programming was found. Agents sent a Notice of Unlicensed Operation to the property-owner, who subsequently reported that the station had been removed from the premises. Continue reading “FCC on Pirate Radio: From Paper Tiger to Puffer Fish”
Tag: new york state broadcasters association
Raids, Bills, Staff Moves: FCC Enforcement Changes Afoot?
The Federal Communications Commission is making new moves to demonstrate the seriousness with which it takes the “problem” of unlicensed broadcasting. This is being reflected in several ways, including the deployment of more tools in field enforcement, legislative activity, and staff changes.
First, enforcement: on Monday, March 26 the agency, in conjunction with Federal Marshals and the Boston Police Department, conducted two station-raids and equipment seizures. Both stations were effectively co-located on the same block of Blue Hill Avenue in the Dorchester neighborhood, which is populated by two-story structures with businesses on the ground floor and apartments above, as well as an old theater which now houses a Baptist church.
In reality, this was an easy two-fer for the FCC: minimum effort expended for maximum impact. The court complaints make for interesting reading. (All publicly available documents involving previous enforcement actions against these stations can be found in our Enforcement Action Database.) Continue reading “Raids, Bills, Staff Moves: FCC Enforcement Changes Afoot?”
FCC Anti-Pirate Enforcement in 2016: Symbolic Inflationism Ahoy

A surprising uptick in the Enforcement Action Database for 2016: 201 total actions were logged last year, which is up from the prior two years. Furthermore, the frequency of threats of fines and actual fines against unlicensed broadcasters also rose: 9 NALs issued for a total of $155,000, and 5 forfeitures handed out for a total of $65,000. We haven’t seen numbers this large since 2014.
It gives some statistical credence to recently-former FCC Chair Tom Wheeler’s assertion that, despite the agency’s admittance that its license-enforcement protocol is effectively broken, it hasn’t ceded the field entirely. Unfortunately, statistics can be fudged, and the FCC’s done that well in the last year. Continue reading “FCC Anti-Pirate Enforcement in 2016: Symbolic Inflationism Ahoy”
NY Broadcasters Try Quantifying Pirates
Tell us something we don’t know: they are pervasive and may outnumber licensed broadcasters in the number one radio market in America.
 That’s the most notable takeaway from a 103-page report (also embedded at the end of this post) prepared for the New York State Broadcasters’ Association by Maryland-based consulting engineers Meintel, Sgrignoli, & Wallace, who camped out at four locales in the NYC metropolitan area — two in NYC proper and two in New Jersey — earlier this year with a cleverly-camouflaged monitoring van (at right) and basically did FM bandscans.
That’s the most notable takeaway from a 103-page report (also embedded at the end of this post) prepared for the New York State Broadcasters’ Association by Maryland-based consulting engineers Meintel, Sgrignoli, & Wallace, who camped out at four locales in the NYC metropolitan area — two in NYC proper and two in New Jersey — earlier this year with a cleverly-camouflaged monitoring van (at right) and basically did FM bandscans.
They picked up 76 pirates on the dial…though they estimate that “there may be more than 100 unauthorized stations” on the air in total. According to the report, this is not the first pirate-survey MS&W has been commissioned for — similar bandscans were conducted in 2012, 2014 and 2015. Compared to last year’s findings, the number of unlicensed broadcasters in Brooklyn alone has increased some 58%, though there’s no way to compare figures since the earlier reports have not been made publicly available. Continue reading “NY Broadcasters Try Quantifying Pirates”
FCC to Congress on Pirate Radio: We Got Nothin'
With little fanfare, the FCC has replied to the Congressional delegations of New York and New Jersey, who are demanding that the agency do something about the proliferation of unlicenesed broadcasters in the New York metropolitan area. At last count, at least three dozen stations are operating in the borough of Brooklyn alone; if you extrapolate that across the five boroughs and add in cities on the New Jersey side of the Hudson River, it’s not inconceivable to estimate that as many as 100 pirate stations may be on the air here.
The rising tide of unlicensed broadcast activity in the NYC area — a trend that is several years old now — is exacerbated by the FCC’s utter lack of resources to deal with the issue. Just last month the agency announced a major restructuring of its field enforcement resources, which will result in a net diminution of boots on the ground across the country. In the NYC metroplex, the number of field agents is being increased by one, from four to five people. Although they will be ostensibly be backed up by one of two flying squads of roving agents who will travel the country to enforcement hot-spots (this includes dealing with many issues other than unlicensed broadcasting), it remains to be seen whether this will meaningfully improve the FCC’s overall enforcement abilities. Continue reading “FCC to Congress on Pirate Radio: We Got Nothin'”
In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?
Can’t say for sure, but the latest update to the Enforcement Action Database seems to suggest it, as the agency considers drastically cutting their already meager ranks. As of the end of April, there’ve been just 35 enforcement actions against 17 stations in four states. There has been no official report of field activity in May. In 2014, there were 52 enforcement actions in the same time-frame.
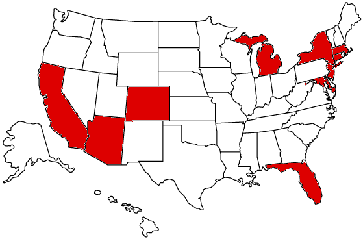 2014 saw the lowest level of FCC enforcement activity against unlicensed broadcasters in nearly a decade. Where agents are active, New York continues to lead the way, followed by New Jersey and California. A station in Colorado also got a warning letter this year, but that was a follow-up to a visit last year. Continue reading “In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?”
2014 saw the lowest level of FCC enforcement activity against unlicensed broadcasters in nearly a decade. Where agents are active, New York continues to lead the way, followed by New Jersey and California. A station in Colorado also got a warning letter this year, but that was a follow-up to a visit last year. Continue reading “In Face of Downsizing, Are FCC Agents Pulling Back?”